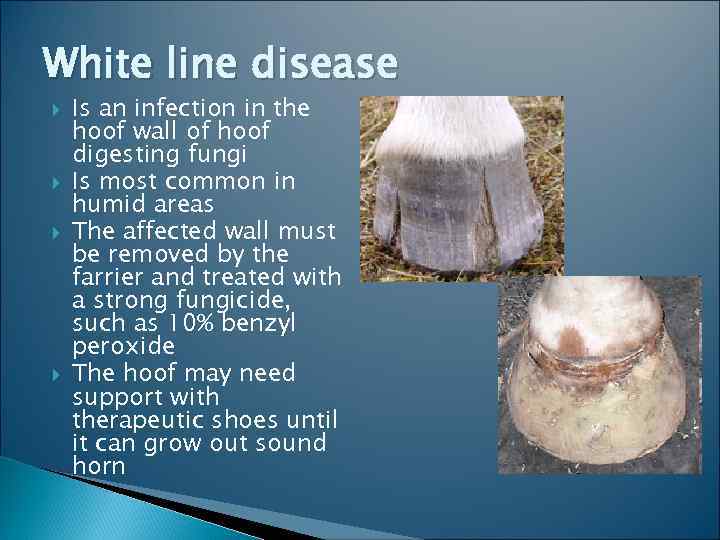
White Line Disease Equine
White line disease equine. So when an invasive organism enters the interior of this weakened hoof its easy for it to take up residence. Kuwano A et al 1999 A survey of white line disease in Japanese racehorses. White line disease is often a mixed fungal and bacterial infection and like thrush its opportunistic said Dr.
Bryan Fraley of Fraley Equine Podiatry at Hagyard Equine Medical Institute. While nearly any horse can get white line disease it is often caused by mechanical environmental physiological or nutritional issues. Signs of White Line Disease Horses can develop WLD in one foot or in all four.
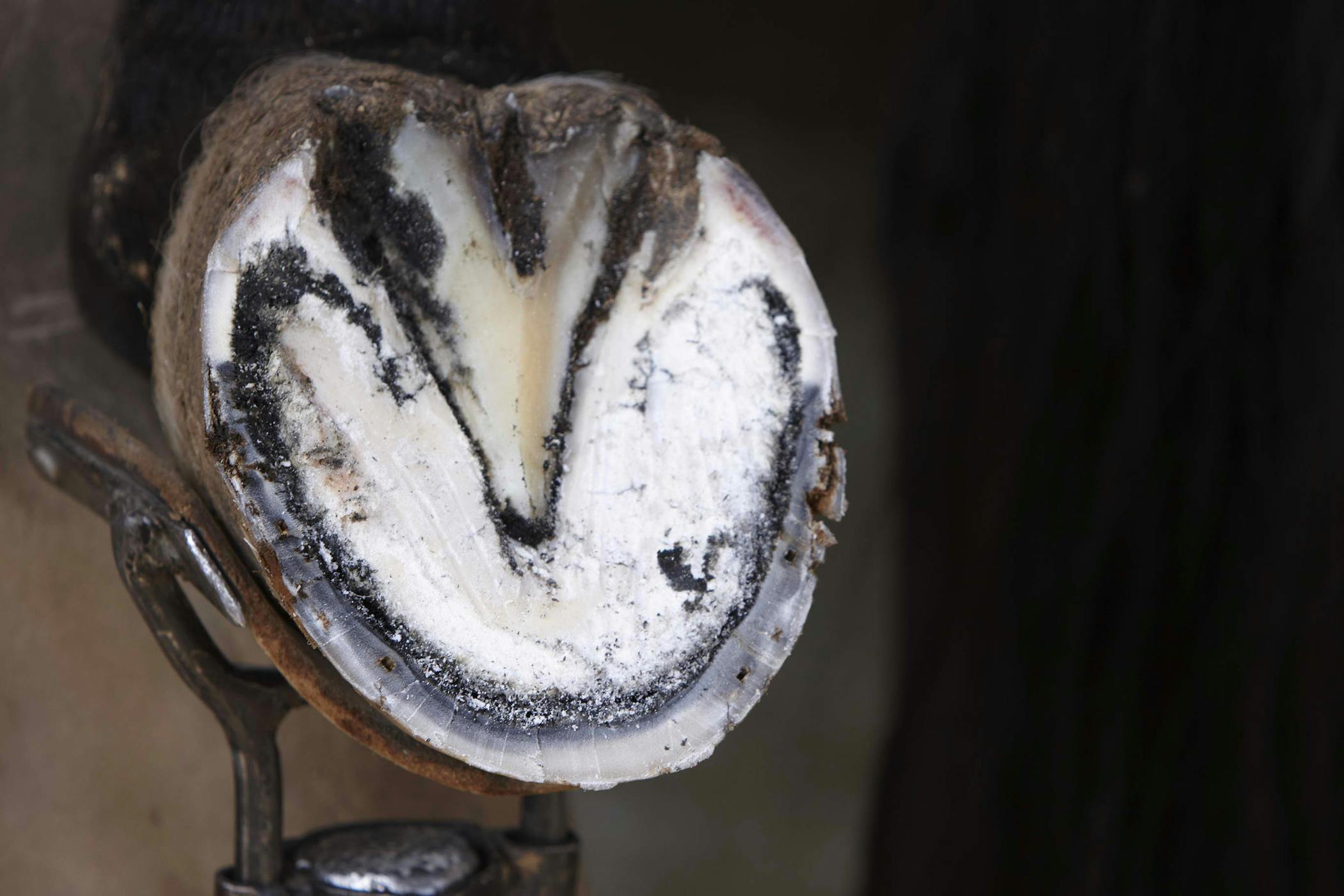
Despite its name the white line is actually more of a cream colour. Equine Vet J 31 6 515-518 PubMed. White line disease is an opportunistic disease.
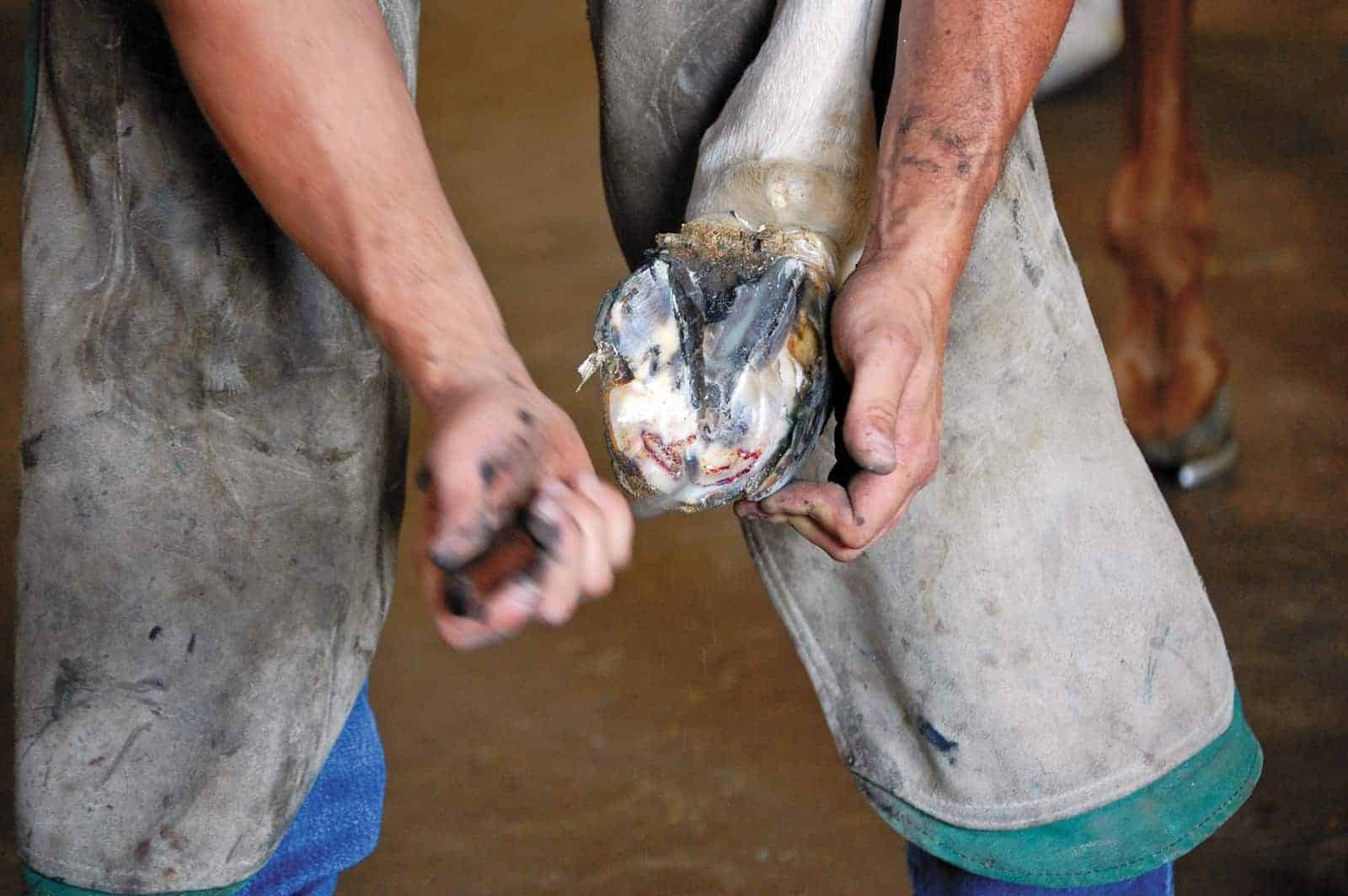
Your farrier will usually notice a powdery hoof wall where there should be a solid junction. Residing in a damp or humid environment Experiencing stress after having had laminitis Injury to his hoof Particularly long toes which can lead to stress in the area where the hoof wall meets the sole of your horses foot Dirty. This infection results in a breakdown of the wall of the hoof which makes shoeing the horse and keeping shoes on difficult.
A closer look at white line disease In a healthy hoof the walls are. A clubby foot results in laminae being stretched to the max every time a horses hoof makes contact with the ground. The following factors can lead to white line disease in your horse.
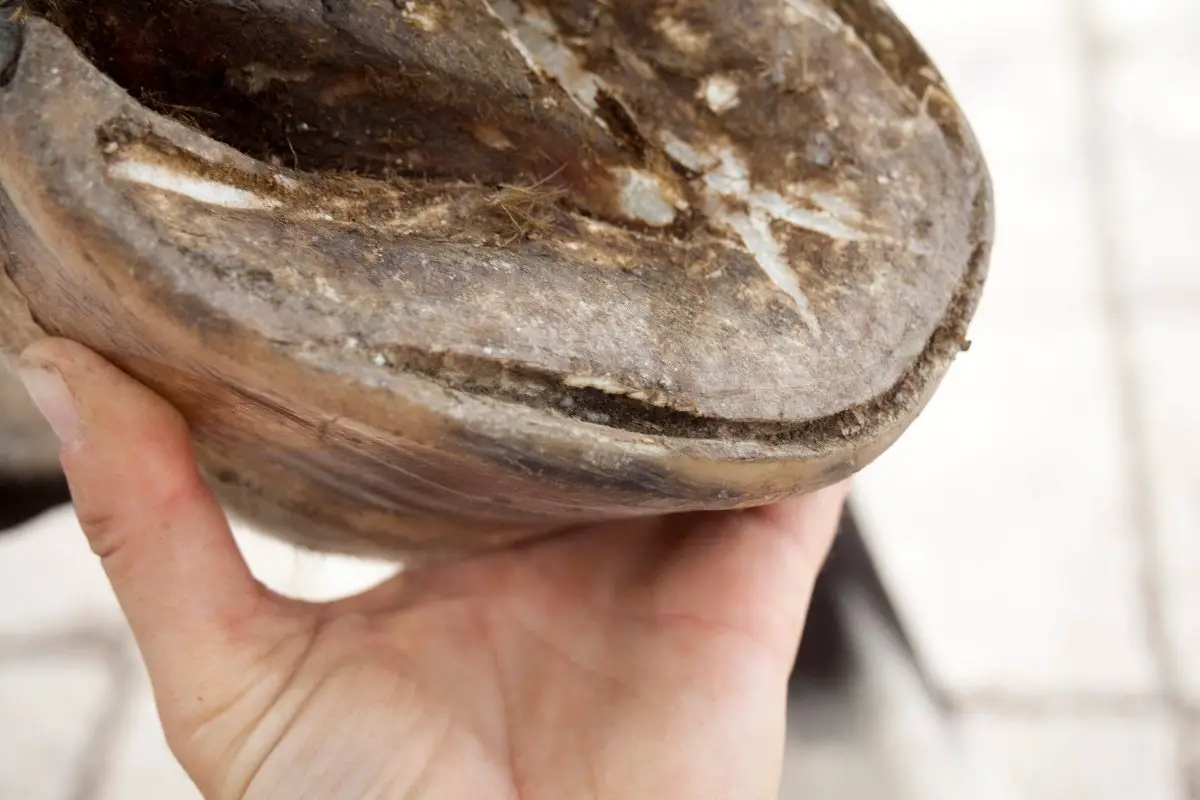
White line disease is a fungal infection of the horses hoof. The telltale signs are stretched white lines and deep grooves filled with rotting material where healthy hoof walls and white lines should be flares that wont grow out hooves that wont hold a shoe persistent wall cracks soles that remain flat. Turner T A 1997 White Line Disease.
Kuwano A et al 1998 Ochomycosis in white line disease in horses - pathology mycology and clinical features. White line disease affects the medial or middle of the hoof wall and can be caused by invading or opportunistic fungus and bacteria pathogens.
Consider this white line disease is merely a symptom revealing that something is amiss in the horses diet lifestyle trim or a combination of these.
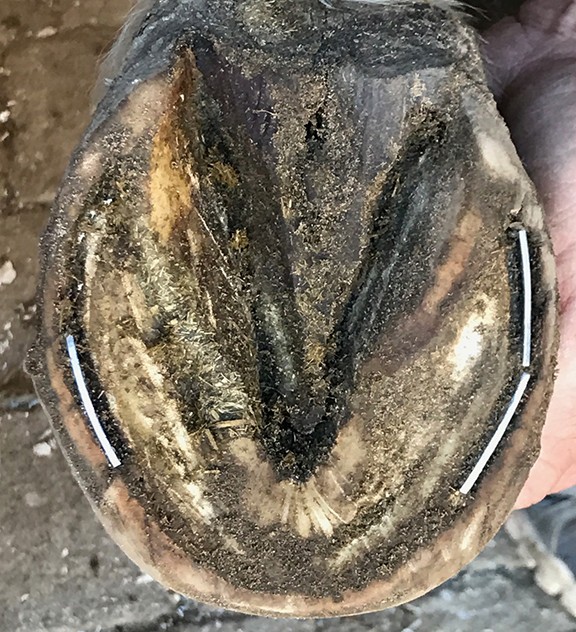
White line disease can affect any horse of any age at any time when conditions are favorable. J Equine Vet Sci 175 236-37 VetMedResource. The part of the hoof known as white line is the inner layer of the wall. So when an invasive organism enters the interior of this weakened hoof its easy for it to take up residence. White line disease is a fungal infection of the horses hoof. In white line disease the hoof wall separates from the underlying laminae stratum internum at the level of the stratum medium tubular horn. Aside from slight crumbling near the white line occasionally a powdery area may arise just behind the white line toward the frog. Consider this white line disease is merely a symptom revealing that something is amiss in the horses diet lifestyle trim or a combination of these. The area may stay small or may gradually widen.
The white line is the narrow light-colored band visible on the underside of a freshly trimmed hoof at the junction of the hoof wall and the sole. OGrady S E 1997 White Line Disease. White line disease affects the medial or middle of the hoof wall and can be caused by invading or opportunistic fungus and bacteria pathogens. J Equine Vet Sci 175 236-37 VetMedResource. Your farrier will usually notice a powdery hoof wall where there should be a solid junction. The area may stay small or may gradually widen. The farrier might also notice a hollow sound when he taps the outside of the hoof wall with a hammer.






































Post a Comment for "White Line Disease Equine"